Pandas DataFrame の列スライスを取る
Manav Narula
2023年1月30日
Pandas
Pandas DataFrame
-
loc()を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする -
iloc()を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする -
redindex()を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする
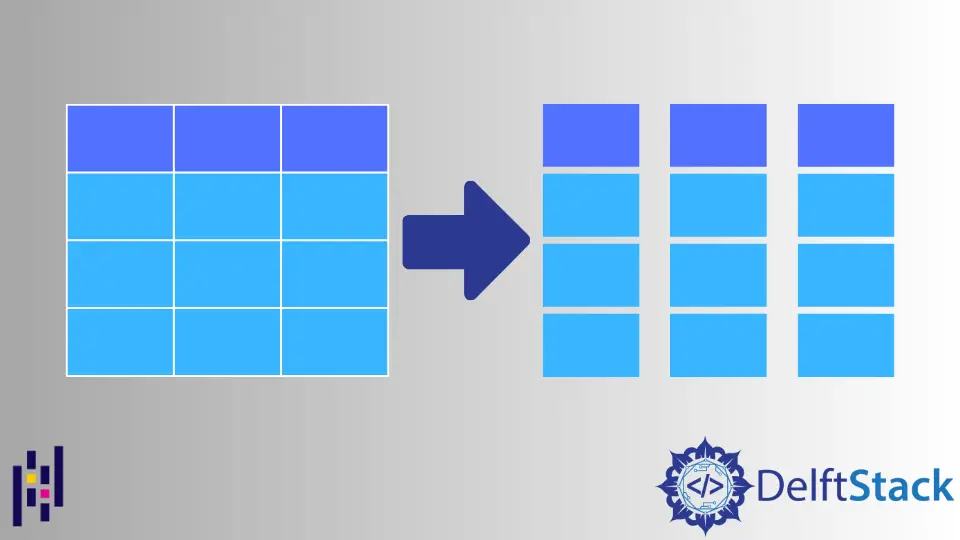
Pandas の列スライシングでは、DataFrame をサブセットにスライスすることができ、必要な列のみを持つオリジナルから新しい Pandas の DataFrame を作成します。ここでは、列スライシングの例として、以下の DataFrame を使って作業を行います。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4, 4), columns=["a", "b", "c", "d"])
print(df)
出力:
a b c d
0 0.797321 0.468894 0.335781 0.956516
1 0.546303 0.567301 0.955228 0.557812
2 0.385315 0.706735 0.058784 0.578468
3 0.751037 0.248284 0.172229 0.493763
loc() を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする
Pandas ライブラリには、列スライシングを行うための複数の方法が用意されています。最初の方法は loc() 関数を使用することです。
Pandas の loc() 関数を使用すると、列名やインデックスラベルを使って DataFrame の要素にアクセスすることができます。loc() を使った列スライシングの構文。
dataframe.loc[:, [columns]]
例:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4, 4), columns=["a", "b", "c", "d"])
df1 = df.loc[:, "a":"c"] # Returns a new dataframe with columns a,b and c
print(df1)
出力:
a b c
0 0.344952 0.611792 0.213331
1 0.907322 0.992097 0.080447
2 0.471611 0.625846 0.348778
3 0.656921 0.999646 0.976743
iloc() を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする
行と列の整数インデックスを用いて DataFrame の要素にアクセスするには、iloc() 関数を用いることもできます。iloc() を用いて列をスライスするための構文を示します。
dataframe.iloc[:, [column - index]]
例:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4, 4), columns=["a", "b", "c", "d"])
df1 = df.iloc[:, 0:2] # Returns a new dataframe with first two columns
print(df1)
出力:
a b
0 0.034587 0.070249
1 0.648231 0.721517
2 0.485168 0.548045
3 0.377612 0.310408
redindex() を使って Pandas DataFrame 内の列をスライスする
reindex() 関数は DataFrame のインデックスを変更するためにも利用でき、列のスライスにも利用できます。reindex() 関数は多くの引数を受け取ることができるが、列スライシングのためには、列名を関数に渡すだけでよい。
reindex() を用いた列スライシングの構文。
dataframe.reindex(columns=[column_names])
例:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4, 4), columns=["a", "b", "c", "d"])
# Returns a new dataframe with c and b columns
df1 = df.reindex(columns=["c", "b"])
print(df1)
出力:
c b
0 0.429790 0.962838
1 0.605381 0.463617
2 0.922489 0.733338
3 0.741352 0.118478
チュートリアルを楽しんでいますか? <a href="https://www.youtube.com/@delftstack/?sub_confirmation=1" style="color: #a94442; font-weight: bold; text-decoration: underline;">DelftStackをチャンネル登録</a> して、高品質な動画ガイドをさらに制作するためのサポートをお願いします。 Subscribe
著者: Manav Narula
Manav is a IT Professional who has a lot of experience as a core developer in many live projects. He is an avid learner who enjoys learning new things and sharing his findings whenever possible.
LinkedIn