Java のバブルソートアルゴリズムを使用して手動リンクリストをソートする
バブルソートは、データ収集のソートに使用される最も一般的なデータ構造アルゴリズムです。隣接する要素が正しくなるまで、間違った順序で繰り返して交換することで機能します。
まず、基本的な並べ替えのデモを示します。次に、Java でリンクリストをソートするための 2つのバブルソートアルゴリズムを実装します。
Java でのバブルソート
並べ替えの算術的な側面に立ち入ることなく、物事を本質的に保ちましょう。バブルソートでは、最初から最後のインデックスまで配列をトラバースします。
そうすれば、現在のインデックスを次のインデックスと比較できるのはそれだけです。この式の中心的な概念は、現在の要素が次の要素よりもサイズが大きくなる場合です。
構文:
for (int A = 0; A < sort - 1; A++)
for (int B = 0; B < sort - A - 1; B++)
if (DEMO[B] > DEMO[B + 1]) {
// Swapping of array
int temp = DEMO[B];
DEMO[B] = DEMO[B + 1];
DEMO[B + 1] = temp;
}
それでは、Java で簡単なバブルソートアルゴリズムを実行してみましょう。ただし、最初に、配列のソートされていないインデックスの初期状態を確認してください。
配列:{43, 65, 21, 64, 12, 6, 1}
次のコードブロックは、この基本的な並べ替えアルゴリズムを適用することにより、この配列インデックスでバブル並べ替えを実行します。
要件に応じて、この式をいつでも変更できることは言及する価値があります。ただし、現時点で明確にするために、コアは基本的なままである必要があります。
コード:
// In this program, we will sort an array DEMO using the bubble sort algorithm
// Main class
public class BubbleSortLinkListExample1 {
// Main function
private void bubbleSort(int DEMO[]) {
// Using .length to determine entire length of array's index
int sort = DEMO.length;
// If array's length is less than int sort, increase it by 1
for (int A = 0; A < sort - 1; A++)
// Formula 1
for (int B = 0; B < sort - A - 1; B++)
if (DEMO[B] > DEMO[B + 1]) {
// Swapping of array
int temp = DEMO[B];
DEMO[B] = DEMO[B + 1];
DEMO[B + 1] = temp;
}
}
/* Now we are going to print DEMO array*/
void printArray(int DEMO[]) {
int sort = DEMO.length;
for (int A = 0; A < sort; ++A) System.out.print(DEMO[A] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// We are going to implement a driver algorithm for sorting our DEMO array
public static void main(String args[]) {
BubbleSortLinkListExample1 ob = new BubbleSortLinkListExample1();
int DEMO[] = {43, 65, 21, 64, 12, 6, 1};
ob.bubbleSort(DEMO);
System.out.println("After the array has been sorted!");
ob.printArray(DEMO);
}
}
この配列を昇順で並べ替えると、Java の出力が得られます。
出力:
After the array has been sorted!
1 6 12 21 43 64 65
Java でのバブルソート手動リンクリスト
リンクリストの手動並べ替えも、バブル並べ替えの簡単な方法です。
以前にデータのトラバースについて説明しましたか?今、私たちはそれを練習します。
ノードを使用すると、あるノードから次のノードにデータを移動できます。
以下のデモモデルをご覧ください。前の例で並べ替えを実行したので、ここでノードを強調することは重要です。
Java でのクラスソートリンクリスト
私たちが理解したように、このクラスを Java のノードを形成するために適用します。
コード:
class SortLL {
public static class Mynode {
int indx;
Mynode fwdMynode;
public Mynode(int indx) {
this.indx = indx;
this.fwdMynode = null;
}
public int getindx() {
return this.indx;
}
}
.setNextNode() 関数も使用します。これらのクラスを個別に使用してオブジェクトを呼び出すことができますが、これは長くて複雑な方法の 1つです。したがって、すべてのクラスを 1つのファイルに保持しました。
同様に、.getNextNode() 関数を使用します。この関数は、引数なしで次のクラス要素を取得します。あなたはその概念に精通している必要があるので、それ以上の苦労なしに手動のバブルソートアルゴリズムを実行しましょう。
-
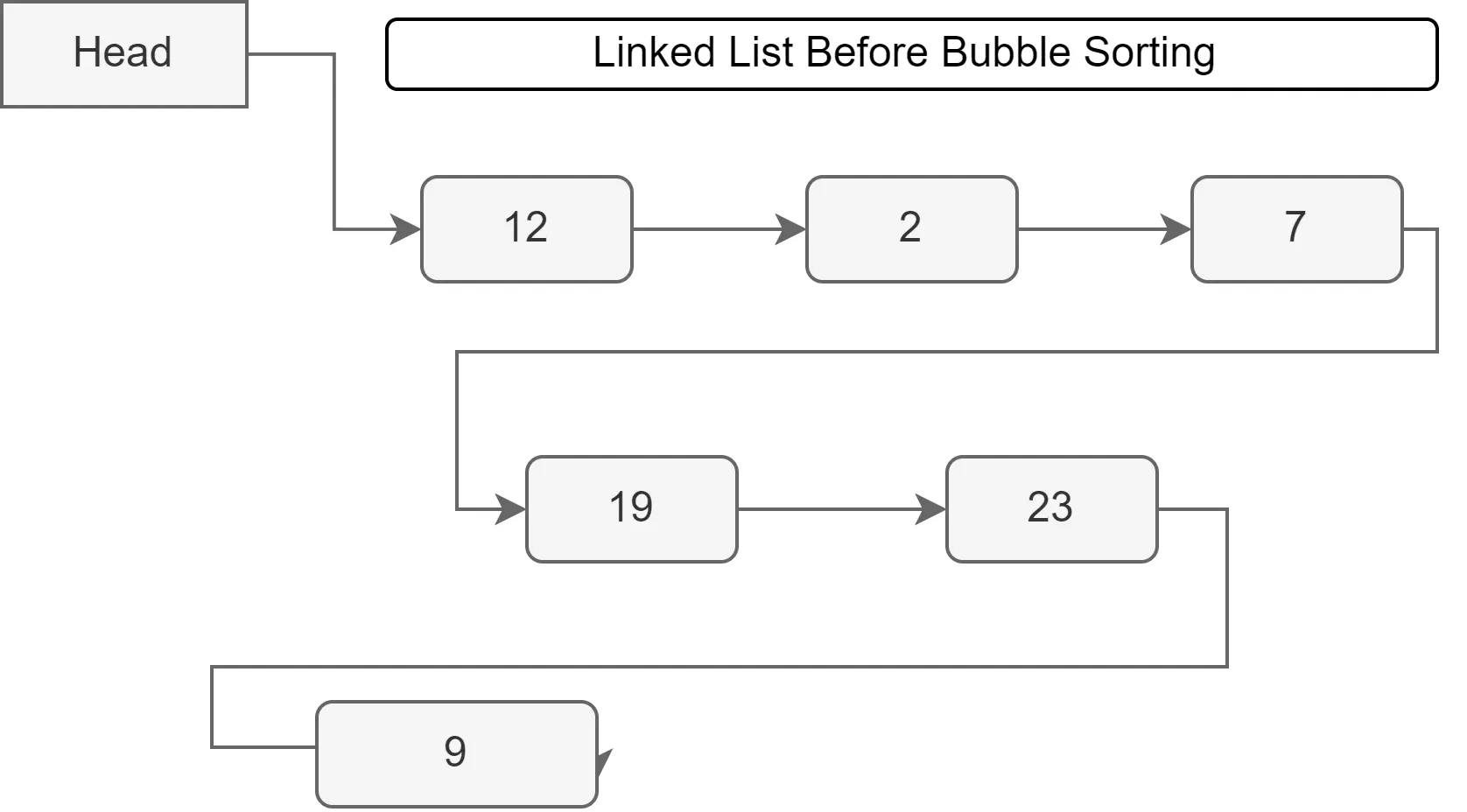
ソート前のリンクリスト:
コード:
```java
class SortLL {
public static class Mynode {
int indx;
Mynode fwdMynode;
public Mynode(int indx) {
this.indx = indx;
this.fwdMynode = null;
}
public int getindx() {
return this.indx;
}
}
// My node class
private Mynode head;
private int size;
public SortLL() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
public void add(int indx) {
Mynode Mynode = new Mynode(indx);
if (head == null) {
head = Mynode;
} else {
Mynode CN = head;
while (CN.fwdMynode != null) {
CN = CN.fwdMynode;
}
CN.fwdMynode = Mynode;
}
size++;
}
public void sort() {
if (size > 1) {
boolean dtr;
do {
Mynode thisMynode = head;
Mynode ladtMynode = null;
Mynode fwd = head.fwdMynode;
dtr = false;
while (fwd != null) {
if (thisMynode.indx > fwd.indx) {
dtr = true;
if (ladtMynode != null) {
Mynode sig = fwd.fwdMynode;
ladtMynode.fwdMynode = fwd;
fwd.fwdMynode = thisMynode;
thisMynode.fwdMynode = sig;
} else {
Mynode sig = fwd.fwdMynode;
head = fwd;
fwd.fwdMynode = thisMynode;
thisMynode.fwdMynode = sig;
}
ladtMynode = fwd;
fwd = thisMynode.fwdMynode;
} else {
ladtMynode = thisMynode;
thisMynode = fwd;
fwd = fwd.fwdMynode;
}
}
} while (dtr);
}
}
public int listSize() {
return size;
}
public void printindx() {
Mynode CN = head;
while (CN != null) {
int indx = CN.getindx();
System.out.print(indx + " ");
CN = CN.fwdMynode;
}
System.out.println();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
}
// indxInterface class
class SrtBubb {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortLL s = new SortLL();
s.add(12);
s.add(2);
s.add(7);
s.add(19);
s.add(23);
s.add(9);
System.out.println("Before Performing Bubble Sort");
s.printindx();
s.sort();
System.out.println("After Performing Bubble Sort");
s.printindx();
System.out.println("Size of the linked list is: " + s.listSize());
}
}
```
-
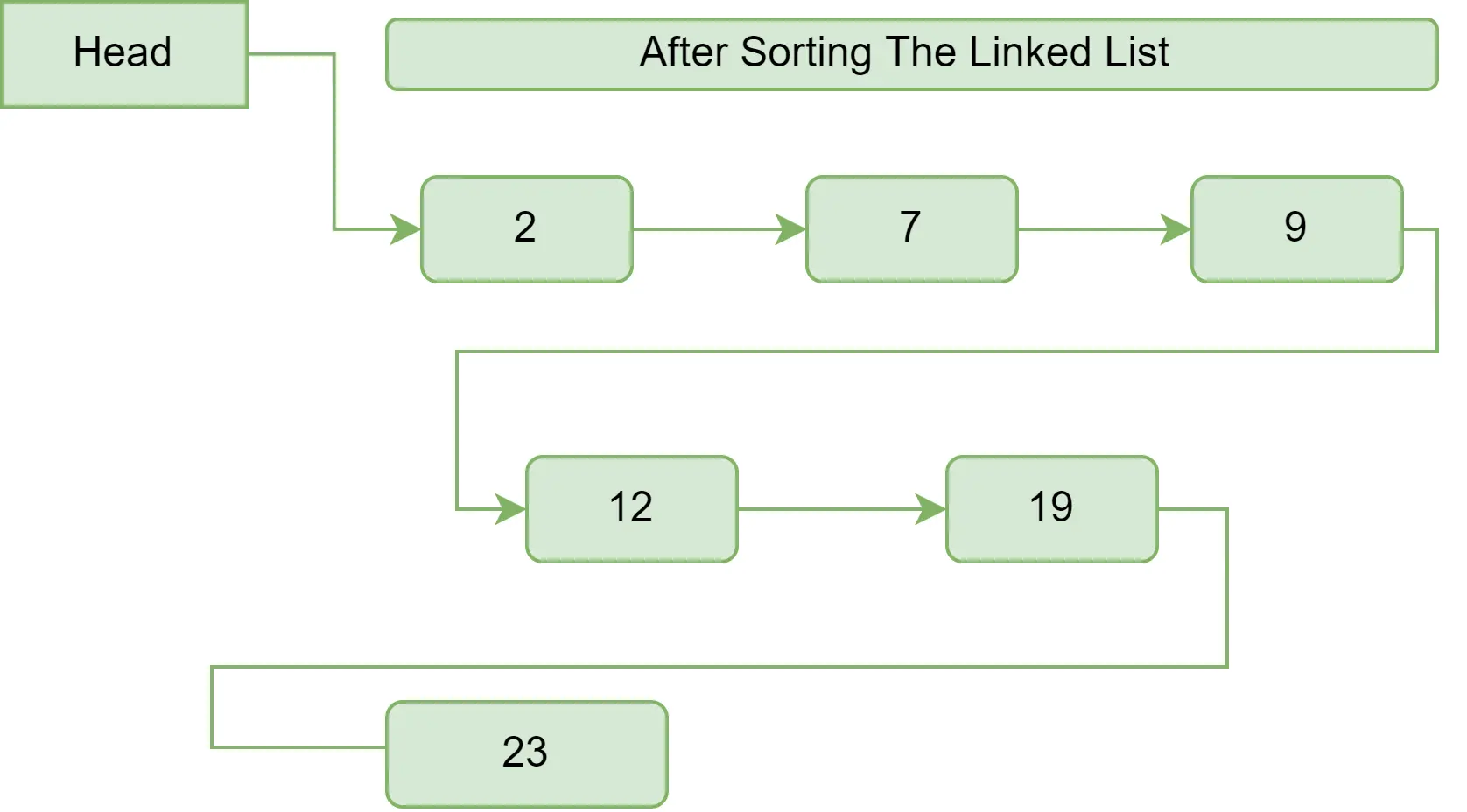
手動のバブルソートを実行した後:
出力:
Before Performing Bubble Sort 12 2 7 19 23 9 After Performing Bubble Sort 2 7 9 12 19 23 Size of the linked list is: 6
要件に基づいてこのプログラムを変更できます。しかし、これは、初心者がバブルソートを使用してリンクリストを手動でソートすることを理解するための最も実用的な方法です。
このトピックについてまだ混乱しているとします。また、ファイルディレクトリにコードを提供しています。
Sarwan Soomro is a freelance software engineer and an expert technical writer who loves writing and coding. He has 5 years of web development and 3 years of professional writing experience, and an MSs in computer science. In addition, he has numerous professional qualifications in the cloud, database, desktop, and online technologies. And has developed multi-technology programming guides for beginners and published many tech articles.
LinkedIn