How to Add Metadata to Pandas Data Frame
Metadata, also known as data about data, is structured data that describes, locates, and manages the content of documents shared on the web through web publishing.
Some web servers and software tools can generate metadata automatically. However, the manual process is also doable.
It can improve a document’s organization, discoverability, accessibility, indexing, and retrieval.
Pandas data frame is a data structure built on top of the data frame that provides the functionality of both R data frames and Python dictionaries.
It is just like a Python dictionary but has all the data analysis and manipulation functionality, like tables in Excel or databases with rows and columns. This tutorial explains adding metadata to Pandas data frames.
Add Metadata to Pandas Data Frame
To add metadata to a data frame, we must meet the below-given requirements.
- Create or import a data frame.
- Read existing metadata of the data frame.
- Add metadata to the data frame.
Create or Import a Data Frame
A data frame is required to add metadata to it. For this purpose, you must install a Python library called pandas.
PS C:\> pip install pandas
Let’s read a data frame from a file using pandas.
Example Code (saved in demo.py):
import pandas as pd
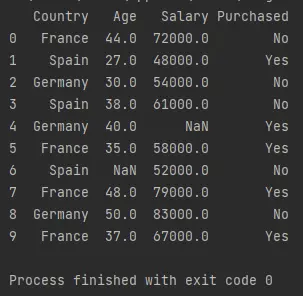
df = pd.read_csv("Data.csv")
print(df)
The above code imports the Python package pandas as pd. The function pd.read_csv() imports a data frame, reads it, and stores it to a variable named df.
Let’s see what pd is.
Output (printed on console):

Read Existing Metadata of the Data Frame
The imported data frame also contains some existing metadata. We can view it through the below-given code examples.
-
Pandas
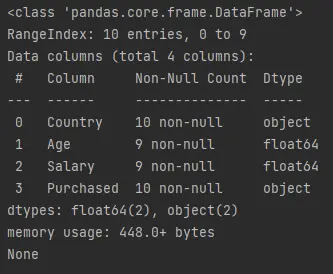
info()function provides a quick summary of the data frame. It retrieves information likemax_cols,memory_usage,show_counts, andnull_counts.Let’s run the below code that calls
df.info()and prints it.Example Code (saved in
demo.py):print(df.info())Output (printed on console):
-
Pandas
columnsattribute returns an immutable n-dimensional array of ordered sets calledIndexthat contains labels of each data frame column. Let’s run the below code that callsdf.columnsand prints anIndex.
Example Code (saved in `demo.py`):
```python
print(df.columns)
```
Output (printed on console):

-
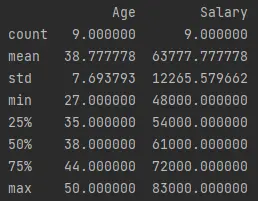
Pandas
describe()function generates descriptive statistics of the data frame. This includescount,mean, and standard deviation asstd,min,max, and percentiles.Let’s run the following code that calls
df.describe()and prints it.Example Code (saved in
demo.py):print(df.describe())Output (printed on console):
Add Metadata to the Data Frame
Let’s run the below code to add metadata to the Pandas data frame.
Example Code (saved in demo.py):
df.audi_car_model = "Q5"
df.audi_car_price_in_dollars = 119843.12
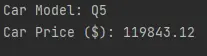
print(f"Car Model: {df.audi_car_model}")
print(f"Car Price ($): {df.audi_car_price_in_dollars}")
Output (printed on console):
Note: Python does not provide a powerful method to propagate metadata to data frames.
For example, operating such as group_by on a data frame with attached metadata will return the previous data frame without attached metadata.
However, you can store the metadata in an HDF5 file for later processing. Let’s run the below code to save metadata in an HDF5 file.
Example Code (saved in demo.py):
def store_in_hdf5(filename, df, **kwargs):
hdf5_file = pd.HDFStore(filename)
hdf5_file.put("car_data", df)
hdf5_file.get_storer("car_data").attrs.metadata = kwargs
hdf5_file.close()
filename = "car data.hdf5"
metadata = {"audi_car_model": "Q5", "audi_car_price_in_dollars": 119843.12}
store_in_hdf5(filename, df, **metadata)
The store_in_hdf5() function performs the following functions:
- Create an
hdf5_fileusing thepd.HDFStore()function with thefilenameas an argument. - Insert the data frame into the file using the
hdf5_file.put()by taking an appropriate name anddfas arguments. - Save metadata to
hdf5_file. It useshdf5_file.get_storer('car_data').attrs.metadataand assignsmetadatato it. - Call
hdf5_file.close()to close the file.
Now, let’s run the below code to import the data frame and metadata from a file.
Example Code (saved in demo.py):
def import_from_file(hdf5_file):
data = hdf5_file["car_data"]
metadata = hdf5_file.get_storer("car_data").attrs.metadata
return data, metadata
filename = "car data.hdf5"
with pd.HDFStore(filename) as hdf5_file:
data, metadata = import_from_file(hdf5_file)
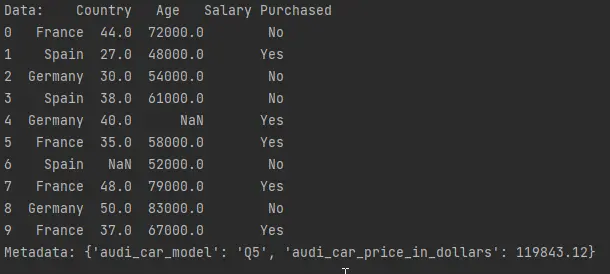
print(f"Data: {data}")
print(f"Metadata: {metadata}")
The import_from_file() function takes the hdf5_file as an argument. It retrieves the following pieces of information:
databy specifying the data’s name inhdf5_file[].metadataby calling themetadataattribute of the functionhdf5_file.get_storer('car_data').attrs.metadata.
Now, we run the Python file demo.py as:
PS C:>python demo.py
It prints the data and metadata returned by the import_from_file() function.
Output (printed on console):