How to Apply a Function to a Column in Pandas Dataframe
-
Pandas
apply()andtransform()Methods -
Use
apply()to Apply a Function to Pandas DataFrame Column -
Use
transform()to Apply a Function to Pandas DataFrame Column
In Pandas, columns and dataframes can be transformed and manipulated using methods such as apply() and transform(). The desired transformations are passed in as arguments to the methods as functions. Each method has its subtle differences and utility.
This article will introduce how to apply a function to a column or an entire dataframe.
Pandas apply() and transform() Methods
Both apply() and transform() methods operate on individual columns and the whole dataframe. The apply() method applies the function along a specified axis. It passes the columns as a dataframe to the custom function, whereas a transform() method passes individual columns as pandas Series to the custom function.
The apply() method’s output is received in the form of a dataframe or Series depending on the input, whereas as a sequence for the transform() method. Both the syntax of the apply() and transform() methods resemble the same as:
Dataframe.apply(customFunction, axis=0)
Dataframe.transform(customFunction, axis=0)
The arguments correspond to
customFunction: the function to be applied to the dataframe or series.axis: 0 refers to'rows', and 1 refers to'columns'; the function needs to be applied on either rows or columns.
Use apply() to Apply a Function to Pandas DataFrame Column
Now we have mastered the basics, let’s get our hands on the codes and understand how to use the apply() method to apply a function to a dataframe column.
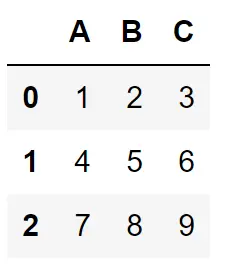
We will use the example dataframe as below.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], columns=["A", "B", "C"])
print(df)
The example code to apply a function to the whole DataFrame is shown below.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], columns=["A", "B", "C"])
print(df)
def add_2(x):
return x + 2
df = df.apply(add_2)
print(df)
Output:
A B C
0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6
2 7 8 9
A B C
0 3 4 5
1 6 7 8
2 9 10 11
As seen above, the function can be applied for the whole of the dataframe.
Apply a Function to a Single Column
Let’s see what happens when the function is applied along a single column.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], columns=["A", "B", "C"])
print(df)
def add_2(x):
return x + 2
df["A"] = df["A"].apply(add_2)
print(df)
# or #
df["A"].transform(add_2)
print(df)
Output:
A B C
0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6
2 7 8 9
A B C
0 3 2 3
1 6 5 6
2 9 8 9
Another Example of Applying a Function to a Single Column
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
roll_no = [501, 502, 503, 504, 505]
data = pd.DataFrame(
{"A": [20, 30, 15, 25, 20], "B": [4, 5, 6, 4, 6], "C": [12, 15, 13, 12, 14]}
)
print("Initial DataFrame:")
print(data)
print("")
updated_df = data.apply(lambda x: x - 5 if x.name == "A" else x)
print("Updated DataFrame:")
print(updated_df)
Output:
Initial DataFrame:
A B C
0 20 4 12
1 30 5 15
2 15 6 13
3 25 4 12
4 20 6 14
Updated DataFrame:
A B C
0 15 4 12
1 25 5 15
2 10 6 13
3 20 4 12
4 15 6 14
Here, we apply the lambda function defined for each column in the DataFrame. The function subtracts every column’s value by 5 only if the name of the column is A.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
roll_no = [501, 502, 503, 504, 505]
data = pd.DataFrame(
{"A": [20, 30, 15, 25, 20], "B": [4, 5, 6, 4, 6], "C": [12, 15, 13, 12, 14]}
)
print("Initial DataFrame:")
print(data)
print("")
data["A"] = data["A"].apply(lambda x: x - 5)
print("Updated DataFrame:")
print(data)
Output:
Initial DataFrame:
A B C
0 20 4 12
1 30 5 15
2 15 6 13
3 25 4 12
4 20 6 14
Updated DataFrame:
A B C
0 15 4 12
1 25 5 15
2 10 6 13
3 20 4 12
4 15 6 14
It applies the lambda function only to the column A of the DataFrame, and we finally assign the returned values back to column A of the existing DataFrame.
Use transform() to Apply a Function to Pandas DataFrame Column
Let’s see how to use the transform() method to apply a function to a dataframe column. We will use the same example dataframe as above.
The example code to apply a function to the whole DataFrame is shown below.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], columns=["A", "B", "C"])
print(df)
def add_2(x):
return x + 2
df = df.transform(add_2)
print(df)
Output:
A B C
0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6
2 7 8 9
A B C
0 3 4 5
1 6 7 8
2 9 10 11
As seen above, the function can be applied to the whole dataframe.
Apply a Function to a Single Column
Let’s see what happens when the function is applied along a single column.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], columns=["A", "B", "C"])
print(df)
def add_2(x):
return x + 2
df["A"] = df["A"].transform(add_2)
print(df)
Output:
A B C
0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6
2 7 8 9
A B C
0 3 2 3
1 6 5 6
2 9 8 9