Auto Increment Values in PostgreSQL
-
Use the
SERIALKeyword to ImplementAUTO_INCREMENTin PostgreSQL -
Use the
GENERATED { BY DEFAULT || ALWAYS} ASClause toAUTO_INCREMENTin PostgreSQL
Auto_Increment in MySQL is a self-incrementing variable that helps give unique identities to data sets inside a table. It is most often used in PRIMARY keys to index rows uniquely.
In MySQL, we can append an AUTO INCREMENT to any column we want.
CREATE TABLE test (
id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
However, today we will learn how to do this in PostgreSQL.
Use the SERIAL Keyword to Implement AUTO_INCREMENT in PostgreSQL
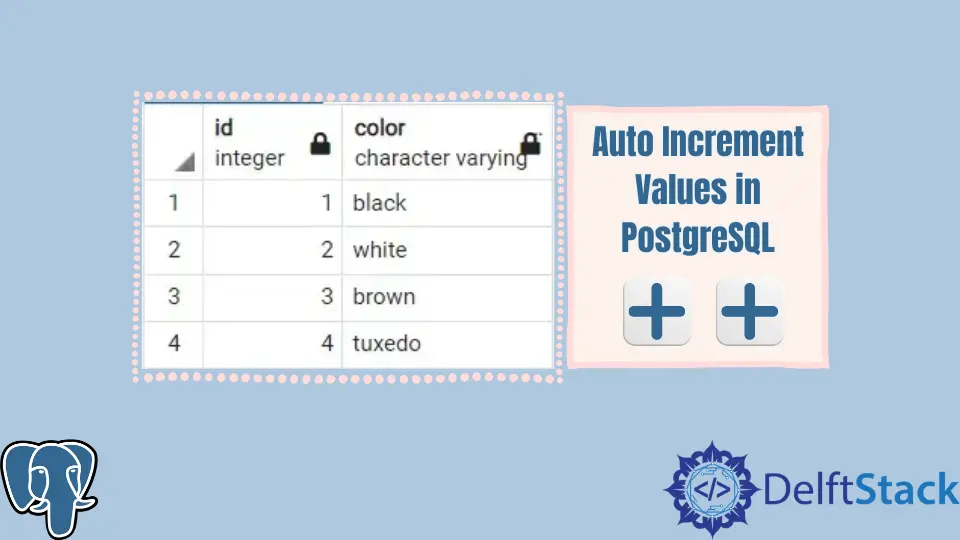
Let’s make a table CAT with an id and a color column.
create table cat(
id SERIAL,
color varchar not null
);
And let’s go ahead and insert some values into it.
insert into cat (color) values('black'), ('white'), ('brown'), ('tuxedo');
Ensure to specify the COLUMN_NAME so that the function does not select all the columns and violates the SERIAL objective. If you dive deeper into the PostgreSQL documentation, you will learn that:

When you click on RUN, it will show the following results.
Output:

Hence, you can see that the SERIAL method effectively implements AUTO_INCREMENT.
a Brief Working of SERIAL and Its Alternatives in PostgreSQL
The SERIAL keyword generates an integer column. Instead of SERIAL, you can also use SERIAL4, representing 4 bytes.
If you want more identifiers or a much bigger range of automatically generated values, you can also use BIGSERIAL or SERIAL8, accommodating up to 2^31 identifiers.
The SERIAL method can be replaced by the following.
create sequence id_col_AI;
create table cat(
id integer DEFAULT nextval('id_col_AI') NOT NULL,
color varchar not null
);
So, what is happening here? The SEQUENCE defines a new number generator. If you want to change the START VALUE to what you like, you can use the START (your number) argument at the declaration’s end.
Then in the ID column, you define it as DEFAULT to get the next value from the generator inside the column. DEFAULT tends to assign a default value other than NULL to the column.
And then, you refer to the SEQUENCE created and call the NEXTVAL(your seq) to get the values in order. This made NOT NULL to prevent any NULL insertions either implicitly or explicitly by the user.
You can also try to extend this to the ALTER TABLE method if your table is already created.
ALTER table cat ALTER id set DEFAULT nextval('id_col_AI');
Use the GENERATED { BY DEFAULT || ALWAYS} AS Clause to AUTO_INCREMENT in PostgreSQL
You may use the following code for adding an auto-incrementing column as well.
id integer generated by default as identity
We use BY DEFAULT rather than ALWAYS because the former tend to have user values written, but the latter only allows system-specified values. You can use ALWAYS as well.
In many systems, it may work perfectly. However, if using ALWAYS returns an error while insertion, append the INSERT clause with OVERRIDING SYSTEM VALUE to allow user-specific values.
insert into cat (color) overriding system value
values('black'), ('white'), ('brown'), ('tuxedo');
This uses an automatically attached sequence such as the random generator mentioned before.
Hello, I am Bilal, a research enthusiast who tends to break and make code from scratch. I dwell deep into the latest issues faced by the developer community and provide answers and different solutions. Apart from that, I am just another normal developer with a laptop, a mug of coffee, some biscuits and a thick spectacle!
GitHub