How to Select Top N Rows in MySQL

Sometimes, you have to select the MySQL database’s top N rows depending on the project requirements.
The value of n varies as per requirements; it can be TOP 1 row or TOP 30 rows. We will learn how to select Top N rows using the LIMIT clause in the MySQL database.
You can benefit from these queries by using them in paging, finding recent purchases or transactions. It is also important to note that every database has a different syntax to get this functionality done.
SQL Server uses SELECT TOP, MySQL uses LIMIT, and Oracle uses ROWNUM and FETCH FIRST n ROWS ONLY.
Select Top N Rows in MySQL Using the LIMIT Clause
Use of Top N query means you want to limit the results to a certain number of rows. These are used to get the best or most recent rows from a result set.
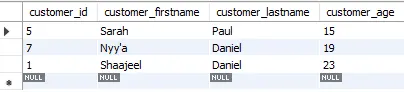
For this tutorial, we are using a table named customer that has customer_id, customer_firstname, customer_lastname, and customer_age. We populated this customer table with some data that looks as follows at the moment.

We will be using the customer table to practice the LIMIT in MySQL. We want to select the TOP 3 records from the customer table.
Example Code:
SELECT * FROM customer LIMIT 3;
Output:

We want to get the three youngest customers and analyze them for forecasting purposes. You can see the following code sample.
Example Code:
SELECT * FROM customer
ORDER BY customer_age ASC
LIMIT 3;
Firstly, the table data will be ordered with respect to the customer_age. The youngest customer will be at the top, and the older one will be at the bottom.
Then select the top 3 rows from the result set of the ordered data. See the following screenshot.
Output:
What if you want to select the top 4 rows starting from offset 3? You can do that by using the following syntax.
SELECT * FROM you_table_name
ORDER BY column_name ASC
LIMIT offset,row_count;
Always remember that the offset for the first row in the LIMIT clause starts from 0. Here is the sample code for this scenario.
Example Code:
SELECT * FROM customer
ORDER BY customer_age ASC
LIMIT 3,4;
Output:

Alternatively, we can also use the LIMIT clause with row count and offset in the following way.
# You can also write the above query in this way
SELECT * FROM person.customer
ORDER BY customer_age ASC
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 4;
Output:

You can also order your table in descending order by replacing the ASC with DESC in the query.
Conclusion
We have concluded that we can limit the number of rows from a result set depending on the project requirements.
We can select the top n number of rows or the top n number of rows that start from m. We also learned that the LIMIT clause could be used with/without ORDER BY.
