How to Convert RGB to Gray Scale in Matlab
- Understanding RGB and Grayscale Images
- Method 1: Manual Conversion to Grayscale
-
Method 2: Using the
rgb2gray()Function - Conclusion
- FAQ
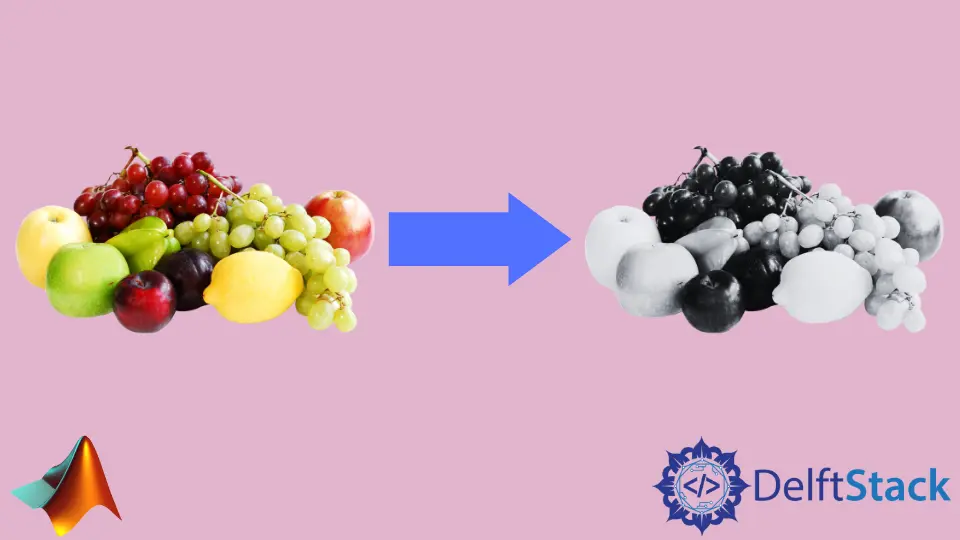
Converting RGB images to grayscale is a common task in image processing, especially when simplifying images for analysis or enhancing certain features. In MATLAB, this can be achieved through two primary methods: manually calculating the grayscale values or utilizing the built-in rgb2gray() function. Understanding these methods not only enhances your MATLAB skills but also provides insight into the underlying principles of image processing.
In this article, we will explore both approaches in detail, ensuring you have the knowledge to effectively convert RGB images to grayscale in MATLAB.
Understanding RGB and Grayscale Images
Before diving into the conversion methods, it’s essential to grasp the concepts of RGB and grayscale images. RGB images are composed of three color channels: Red, Green, and Blue. Each channel contributes to the overall color of a pixel, allowing for a wide range of colors. Conversely, grayscale images consist of varying shades of gray, where each pixel represents intensity rather than color. This simplification can be beneficial for many applications, including edge detection, image analysis, and reducing computational load.
Method 1: Manual Conversion to Grayscale
Converting an RGB image to grayscale manually involves calculating the intensity of each pixel using a weighted formula. The most common formula is:
Gray = 0.2989 * R + 0.5870 * G + 0.1140 * B
This formula accounts for human perception, where the green channel has the most significant impact on brightness. Below is a MATLAB code example demonstrating how to perform this conversion manually.
% Read the RGB image
rgbImage = imread('image.jpg');
% Extract the red, green, and blue channels
R = rgbImage(:, :, 1);
G = rgbImage(:, :, 2);
B = rgbImage(:, :, 3);
% Calculate the grayscale image
grayImage = 0.2989 * R + 0.5870 * G + 0.1140 * B;
% Convert to uint8
grayImage = uint8(grayImage);
% Display the grayscale image
imshow(grayImage);
Output:

In this code, we start by reading an RGB image using imread(). We then extract the individual R, G, and B channels. The grayscale image is computed using the weighted sum of the channels based on the formula mentioned above. After calculating the grayscale values, we convert the result to uint8 format, which is suitable for image display. Finally, we use imshow() to display the grayscale image. This method gives you complete control over the conversion process, allowing for customization if needed.
Method 2: Using the rgb2gray() Function
MATLAB provides a convenient built-in function called rgb2gray() that simplifies the process of converting RGB images to grayscale. This function abstracts the underlying calculations, making it an efficient choice for quick conversions. Here’s how to use it:
% Read the RGB image
rgbImage = imread('image.jpg');
% Convert to grayscale using rgb2gray
grayImage = rgb2gray(rgbImage);
% Display the grayscale image
imshow(grayImage);
Output:

In this example, we read the RGB image just like before. However, instead of manually calculating the grayscale values, we simply call the rgb2gray() function, passing in the RGB image. This function handles the conversion internally, applying the appropriate weights to each color channel. The resulting grayscale image is then displayed using imshow(). This method is especially useful for those who need a quick solution without delving into the details of the conversion process.
Conclusion
Converting RGB images to grayscale in MATLAB can be accomplished through manual calculations or by using the built-in rgb2gray() function. Each method has its advantages: manual conversion offers flexibility and a deeper understanding of image processing, while rgb2gray() provides a quick and efficient solution. Depending on your project requirements, you can choose the method that best suits your needs. With these techniques at your disposal, you can enhance your image processing capabilities and streamline your workflow in MATLAB.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between RGB and grayscale images?
RGB images contain three color channels (Red, Green, Blue), while grayscale images consist of varying shades of gray representing intensity. -
Why would I convert an RGB image to grayscale?
Converting to grayscale simplifies the image, making it easier to analyze and process, especially for tasks like edge detection and image segmentation. -
Can I customize the grayscale conversion in MATLAB?
Yes, by manually calculating the grayscale values, you can adjust the weights applied to each color channel to suit your specific needs. -
Is the
rgb2gray()function available in all versions of MATLAB?
Thergb2gray()function is available in most versions of MATLAB, but it’s always a good idea to check the documentation for your specific version. -
How can I display images in MATLAB?
You can use theimshow()function to display images in MATLAB, whether they are RGB or grayscale.
