How to Get Environment Variables in JavaScript
- Introduction to Environment Variables
-
Use the
envProperty to Get the Environment Variables in JavaScript -
Use the
dotenvPackage to Get the Environment Variables in JavaScript
This article will introduce some methods to get the environment variables in JavaScript.
Introduction to Environment Variables
You can use the environment variables to store different kinds of data your application can use. For example, it could be a database connection, port number, password, secret key, etc.
The use of the environment variables becomes lively when you have to write configurations according to your environment. You can provide different configurations to your application for your development and production environments.
First, let’s see how we can create and get an environment variable from the shell. You can use the export command to pass a variable or a function to a child process.
We can define a variable using the command below.
$ export PORT=8080
Next, we can get the environment variable using the echo command. We need to use the $ sign before the environment variable while printing it.
$ echo $PORT
Output:
8080
The upcoming section will teach you how to access the environment variable in a JavaScript program.
Use the env Property to Get the Environment Variables in JavaScript
We can use the env property provided by the process core module in JavaScript to set the environment variables and then can get the variable.
The env property can create a new environment variable. After setting the environment variable, we can print the variables to the console.
For example, use the following command to initialize a new npm package.
npm init -y
Next, set the following property in the package.json file.
"type": "module"
In JavaScript, import the env property from the process module.
Then, use the env property to set an environment variable as env.PORT and assign a value. After that, print the variable.
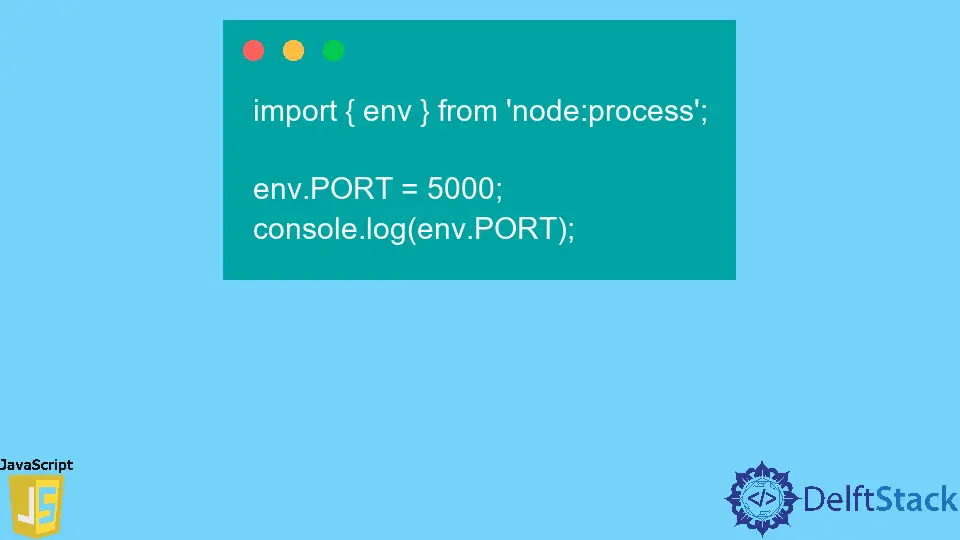
Example Code:
import {env} from 'node:process';
env.PORT = 5000;
console.log(env.PORT);
Output:
5000
Thus, we can create the environment variable and get its value using the env property from the process module in JavaScript.
Use the dotenv Package to Get the Environment Variables in JavaScript
If you are writing a JavaScript application, you might want to use the environment variables. As stated earlier, the environment variable is used to store different kinds of data, and those data can be used in the application.
In such a scenario, you can use the dotenv package. It can read the environment variables set in a .env file and the application.
For example, initialize a package and install the dotenv package. Similarly, create a .env file to store the environment variables.
npm init y
npm install dotenv
touch .env
touch app.js
In the .env file, create an environment variable for the package PORT and set it to 8080 as follows.
PORT=8080
In JavaScript, require the dotenv package and call the config() method. This allows you to access the environment variable stored in the .env file using the process.env property.
Next, use the property to access PORT. Finally, log the expression to the console.
Example Code:
require('dotenv').config();
console.log(process.env.PORT)
Output:
8080
Thus, we can use the dotenv package to get the environment variable in JavaScript.
Subodh is a proactive software engineer, specialized in fintech industry and a writer who loves to express his software development learnings and set of skills through blogs and articles.
LinkedIn